
Recording Conversations Without Consent in Texas | Wiretapping Laws
 With roadway cameras at nearly every street corner, video surveillance in businesses, doorbell cameras on homes, web cams on computers, and recording capabilities on mobile phones – we must navigate carefully in a digital world. We’ve seen titillating news reports exposing a secret audio tape of a public figure having scandalous phone conversations, or video surveillance of questionable traffic stops that escalate in shocking fashion. You may have had a suspicious feeling that you were being recorded, or on the other hand, felt as if you needed to record a conversation with another for your own protection.
With roadway cameras at nearly every street corner, video surveillance in businesses, doorbell cameras on homes, web cams on computers, and recording capabilities on mobile phones – we must navigate carefully in a digital world. We’ve seen titillating news reports exposing a secret audio tape of a public figure having scandalous phone conversations, or video surveillance of questionable traffic stops that escalate in shocking fashion. You may have had a suspicious feeling that you were being recorded, or on the other hand, felt as if you needed to record a conversation with another for your own protection.
With privacy seemingly harder to come by as compared with days long past—what does Texas law say about recording conversations? Is it illegal to record a phone conversation with another person? What about in person?
The short answer is: YES, you can record a conversation with another person without that person’s consent. But this answer requires more explanation.
Recording Phone Calls in Texas | Texas is a One-Party Consent State
Under Texas Law, it is a crime intercept or record any wire, oral or electronic communication without the consent of at least one party. The good news is that you count as one party and if you’re recording then you have probably given yourself consent to record the conversation. Generally speaking, state wiretapping laws turn on whether the state is a one-party consent state. While some states require the consent of all of the parties to a conversation prior to recording, Texas permits the recording of telephone calls, so long as the consent of one of the parties is obtained. As stated, if you are one of the parties on the phone call, then you may consent to having your own conversation recorded—you need not alert the other party. Additionally, a parent may give vicarious consent to the recording of a child’s conversation if the parent has a good faith objectively reasonable belief that the recording is necessary for the welfare of the child.
However, if during a phone call there are multiple parties who are in different states, then be aware that other state laws may require pre-recording consent of all of the parties. In this scenario, if the recording party obtains consent from the other parties before the recording begins, then the recorder is not in violation of wiretapping laws.
See this link to learn more about the various state wiretapping laws.
Recording In-Person Conversations in Texas | Can I Record Someone Else’s Public Conversation?
Texas law (Penal Code §16.02) does not permit you to record in-person communications when the parties have an expectation that such communication is not subject to interception (i.e. If there is a reasonable expectation of privacy). If you wish to record a conversation to which you are not a party, all of the parties must give consent before the recording device is turned on or there must be no reasonable expectation of privacy (e.g. If the recording is taken from your doorbell camera and the parties are standing on you doorstep). If you are a party to the conversation, record away.
Further, you are able to record in-person communication at a public place, like a mall food court or at a football game for example, where parties do not have the expectation of privacy. Remember—if you say it in a public place, within earshot of others who may overhear, you do not have an expectation of privacy in those statements. Generally, such statements may be recorded without violating that state’s wiretapping laws.
A Word of Caution of Recording Conversations in Texas
Please be aware that there are both federal and state wiretapping laws that may limit your ability to making recordings of telephone calls or in person conversations. This article addresses state wiretapping laws in Texas only. Additionally, if a person has violated a state or federal wiretapping statute, he may be both charged criminally and be sued civilly by the damaged party.
Further, while a person may have successfully recorded a conversation under state and federal wiretapping laws, the act of disclosing the recording to other third parties could be, in and of itself, punishable criminally or civilly under other legal theories (such as slander, for example).
If you are faced with a wiretapping charge, or have questions about wiretapping, please contact an attorney who will address both the state and federal regulations as they are related to the facts of your specific case. Wiretapping charges are potentially serious felonies that could land a person in jail or prison, with fines ranging from $200 to $10,000. If you are faced with charges related to wiretapping in Texas, please contact our offices at (817) 993-9249 for a consultation.
Summary on Texas Wiretapping
- A person can record a conversation to which you are a party in Texas without violating wiretapping laws, so long as the other party is in a “one party consent” state.
- A person can record a conversation (to which he is not a party) if one of the participants gives him permission.
- A person can record a conversation when, in a public setting, the participants do not have a reasonable expectation of privacy.
- It is almost always illegal to record a phone call or private conversation to which one is not a party, does not have consent from at least one of the parties, and could not naturally overhear the conversation.
This article is for educational purposes only and should never be substituted for legal advice.

 Have you sustained property damage in a powerful storm? If so, you probably had to call a contractor to do necessary repairs. It is sometimes customary in the construction industry for contractors to ask homeowners to pay for some of the work up front, and pay the remaining balance upon completion. Some contractors will ask you to fork over a hefty deposit to someone you do not know, yet you are trusting to get the job done. You are not alone. The good news is that most contractors will operate above the board. Even though social media reviews and ratings sites, such as
Have you sustained property damage in a powerful storm? If so, you probably had to call a contractor to do necessary repairs. It is sometimes customary in the construction industry for contractors to ask homeowners to pay for some of the work up front, and pay the remaining balance upon completion. Some contractors will ask you to fork over a hefty deposit to someone you do not know, yet you are trusting to get the job done. You are not alone. The good news is that most contractors will operate above the board. Even though social media reviews and ratings sites, such as 
 Texas law is clear that every driver must maintain financial responsibility (auto insurance). But, the truth of the matter is that there are thousands of drivers on Texas roads who are underinsured with a minimum policy or not insured at all. What this means is that if you are hit and injured in a car wreck by one of these uninsured or underinsured drivers, you may have to use your own insurance to pay for your medical bills, lost wages, lost ability to work and/or other damages.
Texas law is clear that every driver must maintain financial responsibility (auto insurance). But, the truth of the matter is that there are thousands of drivers on Texas roads who are underinsured with a minimum policy or not insured at all. What this means is that if you are hit and injured in a car wreck by one of these uninsured or underinsured drivers, you may have to use your own insurance to pay for your medical bills, lost wages, lost ability to work and/or other damages.

 This was the 5th year for our law firm to offer scholarships. In honor of the sacrifices of our military veterans, we decided to that the scholarships should be connected to military service. The first scholarship is a $500 award for a
This was the 5th year for our law firm to offer scholarships. In honor of the sacrifices of our military veterans, we decided to that the scholarships should be connected to military service. The first scholarship is a $500 award for a 
 Many people involved in motor vehicle collisions may not have police or accident reports documenting the specifics of the wreck. Sometimes it could be because the wreck was not reported and the police were never called. Other times, the police may have been called but simply did not respond. Law enforcement agencies often lack the resources to respond to each and every car wreck that occurs in their jurisdiction. More and more police agencies are putting policies into place that do not require them to respond to what the agency deems a “minor” wreck. The problem is that sometimes a wreck that law enforcement deems “minor” may actually have major long-term consequences (and injuries) for the individuals involved.
Many people involved in motor vehicle collisions may not have police or accident reports documenting the specifics of the wreck. Sometimes it could be because the wreck was not reported and the police were never called. Other times, the police may have been called but simply did not respond. Law enforcement agencies often lack the resources to respond to each and every car wreck that occurs in their jurisdiction. More and more police agencies are putting policies into place that do not require them to respond to what the agency deems a “minor” wreck. The problem is that sometimes a wreck that law enforcement deems “minor” may actually have major long-term consequences (and injuries) for the individuals involved.
 Rideshare companies like Lyft and Uber have risen to prominence over the last several years, grabbing a sizable market share from traditional taxi cab and town car companies. Additionally, there has been a surge in food delivery services (like DoorDash) and contract delivery drivers for Amazon. With more and more of these companies offering rides and deliveries from their part-time drivers, we are also seeing accidents involving the drivers for these companies. These accidents can sometimes have confusing liability issues that accompany them. It is important to know how to proceed and what you are entitled to if you are involved in an accident with a rideshare driver, as a passenger or another driver.
Rideshare companies like Lyft and Uber have risen to prominence over the last several years, grabbing a sizable market share from traditional taxi cab and town car companies. Additionally, there has been a surge in food delivery services (like DoorDash) and contract delivery drivers for Amazon. With more and more of these companies offering rides and deliveries from their part-time drivers, we are also seeing accidents involving the drivers for these companies. These accidents can sometimes have confusing liability issues that accompany them. It is important to know how to proceed and what you are entitled to if you are involved in an accident with a rideshare driver, as a passenger or another driver.

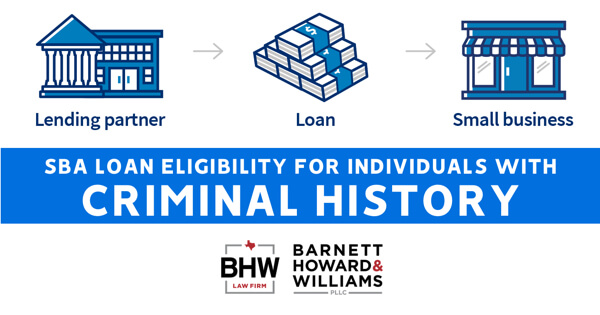
 Countless small businesses have been impacted by the
Countless small businesses have been impacted by the 
 With the declaration of a state of disaster in Texas by Governor Greg Abbott on March 13,2020 comes some new consequences that Texas citizens need to be aware of.
With the declaration of a state of disaster in Texas by Governor Greg Abbott on March 13,2020 comes some new consequences that Texas citizens need to be aware of.
 On March 13, 2020,
On March 13, 2020, 
 There are some criminal offenses that require the state the prove that the defendant acted “recklessly” or with “criminal recklessness.” In a colloquial sense, we (including prosecutors) often think of recklessness as another word for carelessness, but it actually has a specific definition in the Texas Penal Code.
There are some criminal offenses that require the state the prove that the defendant acted “recklessly” or with “criminal recklessness.” In a colloquial sense, we (including prosecutors) often think of recklessness as another word for carelessness, but it actually has a specific definition in the Texas Penal Code.





