
 “Sexting” has become a very popular activity amongst teenagers and young adults in the last several years. This generation sees it as just another ordinary part of life with cell phones. For parents, prosecutors, and law enforcement officers, however, sexting is a dangerous habit that has wide-ranging effects. While sexting has the potential to severely damage lives and reputations, the very nature of it makes it difficult for authorities to adequately address the problems it causes. This article will explore what sexting is, how common it is, the applicable laws, and the practical implications of applying those laws to common instances of sexting.
“Sexting” has become a very popular activity amongst teenagers and young adults in the last several years. This generation sees it as just another ordinary part of life with cell phones. For parents, prosecutors, and law enforcement officers, however, sexting is a dangerous habit that has wide-ranging effects. While sexting has the potential to severely damage lives and reputations, the very nature of it makes it difficult for authorities to adequately address the problems it causes. This article will explore what sexting is, how common it is, the applicable laws, and the practical implications of applying those laws to common instances of sexting.
What Is Sexting?
Sexting is derived from the words “sex” and “texting.” It means the sending of nude or sexually explicit photos or sexually suggestive text messages by text, email, or instant messenger using a mobile device. Many times, the person depicted in the photographs has either consented to the photo being taken or has taken the pictures of themselves. Typically, the person in the photograph, either on their own initiative or at the request of another, takes the photo and then voluntarily sends it to a significant other or a person they are attracted to. The intent is generally for the picture to be kept private by the initial recipient.
The problem with sexting arises when the photograph is either posted on the internet, usually through a social media platform, or is shared with others through text or email. In many cases, this posting or sharing is not consented to by the person depicted in the picture.
How Common is Sexting?
A study done by Drexel University in 2015 found that over 80% of adults surveyed admitted to sexting within the last year. The study was presented during the American Psychological Association’s 2015 convention. According to GuardChild.com, 20% of all teenagers have sent or posted nude or semi-nude photos or videos of themselves and 39% of teenagers have sent sexually suggestive messages through either email, text, or instant messaging.
Criminal Laws Applicable to Texting in Texas
In the State of Texas, there are several laws which could be used to prosecute instances of sexting, especially if it involves a minor. These laws can range from a Class C misdemeanor to a first-degree felony.
Unlawful Disclosure or Promotion of Intimate Visual Material
Texas law makes it unlawful for a person to intentionally disclose photographs or videos of a person engaged in sexual conduct or with their intimate parts exposed without the consent of the person depicted if the person in the photo/video had a reasonable expectation that the material would remain private, the person depicted is harmed and the identity of the person in the photo/video is revealed through the disclosure. This is a Class A misdemeanor.
Sale, Distribution, or Display of Harmful Material to a Minor
A person who sells, distributes, or shows “harmful material” to a minor, knowing that the material is harmful and the person is a minor, or displays harmful material and is reckless about whether a minor is present who would be offended is guilty of this offense in Texas. This is a Class A misdemeanor unless the person uses a minor to commit the offense, and then it is a third-degree felony.
Sexual Performance by a Child
The offense of sexual performance of a child is committed when a person employs, authorizes, or induces a child under the age of 18 to engage in sexual conduct. In this context, “sexual conduct” includes the lewd exhibition of the genitals, anus or breast. This offense is a third-degree felony, but if the victim was under the age of 14 at the time of the offense, then it is enhanced to a second-degree felony.
Possession or Promotion of Child Pornography
A person commits the offense of possession or promotion of child pornography if he intentionally or knowingly promotes or possesses with the intent to promote material that depicts a child engaged in sexual conduct knowing that the material depicts a child. This is a third-degree felony, but it can be enhanced to a second or first-degree felony.
The Sexting Law – Electronic Transmission of Certain Visual Material Depicting Minor
This is Texas’ “sexting” statute. Under it, a person under the age of 18 commits an offense if he intentionally or knowingly possesses or promotes to another minor visual material that depicts a minor engaged in sexual conduct by electronic means if he produced the material or knows that another minor produced it. This is a Class C misdemeanor, but it can be enhanced to either a Class B or Class A misdemeanor in certain situations.
Practical Implications
An instance of sexting in Texas can be prosecuted under any of the above laws. However, there are problems with each of these statutes that makes it difficult to prosecute sexting cases under them. These problems are what led the Texas legislature to create the sexting law several years ago.
Problems with the Sexting Law
However, there are two major problems with this law. First, the sexting statute only applies to persons under the age of 18. This means that an 18-year-old high school student who shares sexting photos with others in his high school cannot be prosecuted under this law. The second problem with it is that it creates a defense to prosecution if the person in possession of the visual material destroys it. So, the law that makes sexting illegal also allows those who break the law to get away with it by destroying the evidence. Because of these problems, it is almost impossible to prosecute someone under this law.
Problems with Using the Other Laws to Prosecute Sexting
The main issue with using the other laws laid out above to prosecute sexting cases is that they were not created to address this specific behavior. So, it becomes a situation where prosecutors are having to shove a square peg into a round hole to make it work in many cases. For instance, the Unlawful Disclosure or Promotion of Intimate Visual Material law requires that the person in the pictures had a reasonable expectation that the photos would remain private. GuardChild.com found in their compilation of sexting statistics that 44% of teenagers believe it is common for sexually suggestive text messages to be shared with others, and 35-40% of them feel that it is common for nude or semi-nude photos to be shared with others beyond the intended recipient. These beliefs undermine the “reasonable expectation of privacy” prong of the law.
Similarly, the Possession or Promotion of Child Pornography statute is problematic when used in sexting cases because it does not include any protections from prosecution for the victim. This means that when a teen age girl takes a nude photo of herself and sends it to her boyfriend, who then shares it with other students, the girl who took the photo of herself is as guilty of promotion of child pornography as the boy who shared it with others. Most people would agree that the victim shouldn’t face charges for child pornography. Yet, prosecutors must either prosecute both of them or do nothing.
Sex Offender Registration for a Sexting Conviction
Another major practical ramification of sexting is that if a person is convicted or adjudicated for sexting under the possession or promotion of child pornography law, he will be required to register as a sex offender for life if the person is prosecuted in the adult system or for ten years past the end of his sentence if he is adjudicated as a juvenile. Depending on the facts of the case, this can be a very harsh consequence for a behavior that is so common in this modern world we live in. But it is important for anyone who engages in sexting, and their parents, to realize that sex offender registration for life is a very real possibility if prosecuted.
Conclusion
While many parents may not know that sexting even exists, the fact remains that it is much more common than we would like to think. It can have devastating consequences for the person depicted in the photos, and for anyone who shares or possesses these photos. Many teenagers engage in this behavior without realizing what the ramifications can be.
This is one area where the law hasn’t caught up to technology yet. So, the job of protecting our children from the harms associated with sexting still falls primarily to parents. It is important for parents to educate themselves about the practice and then talk to their teenagers and pre-teens about the dangers of sexting.
Fort Worth Sexual Crimes Defense AttorneyRating: ★★★★★ 5 / 5 starsRated By Google User
“This firm was a Godsend in handling our case!”

 You may have heard of sleepwalking, or sleeptalking, but what about sleep sex? The idea of sleep sex or “sexsomnia” is typically worth a few laughs when you first hear about it, but it is a
You may have heard of sleepwalking, or sleeptalking, but what about sleep sex? The idea of sleep sex or “sexsomnia” is typically worth a few laughs when you first hear about it, but it is a 
 It’s no secret that there are certain offenses that require individuals to register themselves on the sex offender registry. However, what are those offenses? How long is a person required to register?
It’s no secret that there are certain offenses that require individuals to register themselves on the sex offender registry. However, what are those offenses? How long is a person required to register?
 Imagine this: You receive a call out of the blue from a detective telling you that he is investigating your 11-year-old son for sexually touching your 6-year-old niece. How do you protect your young son who is being charged with Aggravated Sexual Assault of a Child? How do you choose between helping your son and helping your niece? Is there any way to get them both help without prosecuting your son? Will your son be labeled a sex offender for the rest of his life? Is there any way for your extended family to work this out?
Imagine this: You receive a call out of the blue from a detective telling you that he is investigating your 11-year-old son for sexually touching your 6-year-old niece. How do you protect your young son who is being charged with Aggravated Sexual Assault of a Child? How do you choose between helping your son and helping your niece? Is there any way to get them both help without prosecuting your son? Will your son be labeled a sex offender for the rest of his life? Is there any way for your extended family to work this out?
 On February 8, 2016, President Obama signed
On February 8, 2016, President Obama signed 
 United States v. Schofield
United States v. Schofield

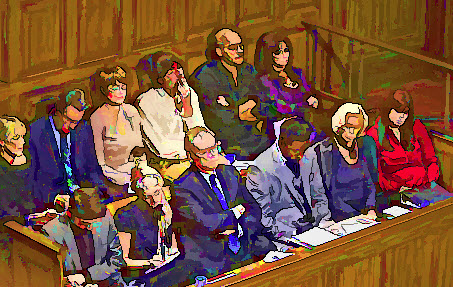
 A felony jury trial in Texas requires 12 jurors (with limited exceptions). The defense can waive that requirement under certain circumstances, and jurors can be excused under certain circumstances. But generally, a felony jury panel must have 12. Below, we discuss a case in Denton County where the jury started with 12 and then went to 11 because a juror could not understand the English language well enough to serve.
A felony jury trial in Texas requires 12 jurors (with limited exceptions). The defense can waive that requirement under certain circumstances, and jurors can be excused under certain circumstances. But generally, a felony jury panel must have 12. Below, we discuss a case in Denton County where the jury started with 12 and then went to 11 because a juror could not understand the English language well enough to serve.
 Texas courts have routinely held that an expert witness, such as a child psychologist, may not offer an opinion about the truth of a certain child victim’s specific allegations or about the truth of child victim allegations in general. But they haven’t shut that door completely.
Texas courts have routinely held that an expert witness, such as a child psychologist, may not offer an opinion about the truth of a certain child victim’s specific allegations or about the truth of child victim allegations in general. But they haven’t shut that door completely.





